HAProxy Coraza SPOA
Overview
Coraza SPOA runs the Coraza Web Application Firewall (WAF) as a backing service for HAProxy. It already embeds the Coraza Engine and processes requests for HAProxy.
There are multiple components involved in the request processing, so here are some terms you should know:
HAProxy includes a Stream Processing Offload Engine (SPOE) to offload request processing to a Stream Processing Offload Agent (SPOA). Data is exchanged between the HAProxy filter and the agent via a binary protocol over TCP called the Stream Processing Offload Procotol (SPOP).
HAProxy forwards incoming HTTP Requests and the Responses to the agent (SPOA) for WAF processing, a message is returned by the agent with the result of the scan.
The following diagram shows a HTTP Request & Response flow: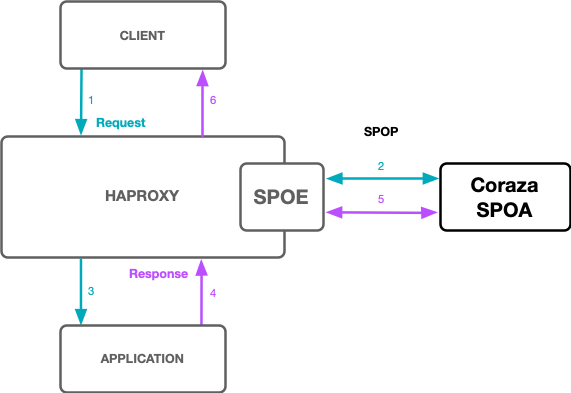
Building the Agent
If you wish to complile Coraza SPOA from source, you’ll first need Go installed
on your machine. Go version 1.16+ is required. Additionally you will need to
install: pkg-config make gcc.
Clone the coraza-spoa repository:
git clone https://github.com/corazawaf/coraza-spoa.git
To compile a development version of coraza-spoa, run make. This will download
all dependencies and compile a coraza-spoa binary.
Configuration Overview
Since the configuration is split-up in a couple of files, here is a quick rundown:
- /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg - HAProxy Main Configuration
- /etc/haproxy/coraza.cfg - HAProxy SPOE Configuration
- /etc/coraza-spoa/config.yml - Coraza SPOA Main Configuration
- /etc/coraza-spoa/coraza.conf - Coraza Engine Configuration
To perform the configuration:
Start by adding a filter statement to an HAProxy frontend, which turns on stream processing. The filter links to a separate SPOE configuration file, in which you configure how HAProxy SPOE communicates with the Coraza SPOA agent.
Coraza SPOA main configuration file is in /etc/coraza-spoa/config.yml.
The following diagram shows how all of the configuration files are linked and
which component they configure.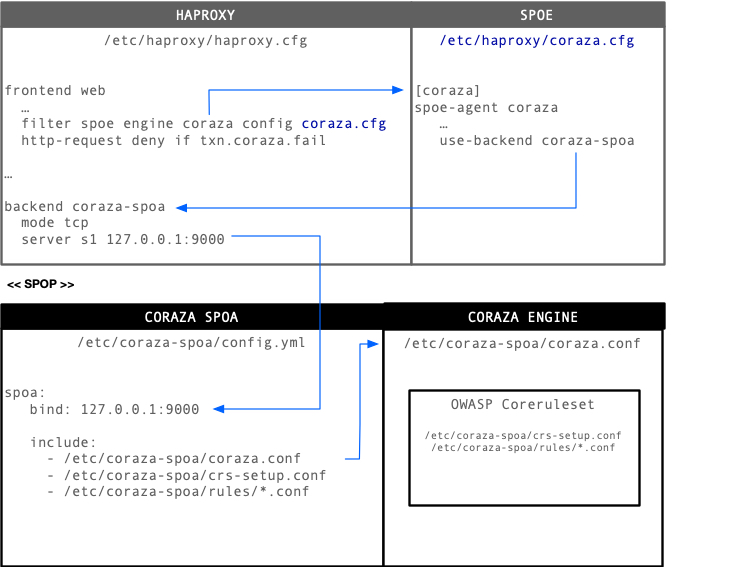
HAProxy Configuration
Below is a example haproxy.cfg configuration:
global
log stdout format raw local0
defaults
log global
option httplog
frontend test
mode http
bind *:80
unique-id-format %[uuid()]
unique-id-header X-Unique-ID
log-format "%ci:%cp\ [%t]\ %ft\ %b/%s\ %Th/%Ti/%TR/%Tq/%Tw/%Tc/%Tr/%Tt\ %ST\ %B\ %CC\ %CS\ %tsc\ %ac/%fc/%bc/%sc/%rc\ %sq/%bq\ %hr\ %hs\ %{+Q}r\ %ID\ spoa-error:\ %[var(txn.coraza.error)]\ waf-hit:\ %[var(txn.coraza.fail)]"
filter spoe engine coraza config coraza.cfg
# Deny for Coraza WAF hits
http-request deny if { var(txn.coraza.fail) -m int eq 1 }
http-response deny if { var(txn.coraza.fail) -m int eq 1 }
# Deny in case of an error, when processing with the Coraza SPOA
http-request deny deny_status 504 if { var(txn.coraza.error) -m int gt 0 }
http-response deny deny_status 504 if { var(txn.coraza.error) -m int gt 0 }
use_backend test_backend
backend test_backend
mode http
http-request return status 200 content-type "text/plain" string "Welcome!\n"
backend coraza-spoa
mode tcp
server s1 127.0.0.1:9000
The HAProxy SPOE gets activated by the filter statement in frontent test.
Configuration of the SPOE behavior is then defined in coraza.cfg. This
includes messages to exchange, which backend HAPRoxy should use internally to
exchange messages with the SPOA, and some other details.
After a HTTP Request or Response has been scanned by the Coraza Engine, it will
inform HAProxy by setting the txn.coraza.fail variable. For scored requests
the variable is set to 1 and the request should get blocked, clean requests
should pass if txn.coraza.fail is set to a value of 0.
Blocking a HTTP Request or Response is handled in the HAProxy frontend test
configuration via the http-request deny and http-response deny
statements.
Additionally in case the Coraza SPOA failed processing the request, it will get
blocked with a deny_status 504. By default HAProxy would just disable the
filter if Coraza takes too long to process the request.
HAProxy SPOE Configuration
The HAProxy SPOE is configured in the /etc/haproxy/coraza.cfg:
# https://github.com/haproxy/haproxy/blob/master/doc/SPOE.txt
[coraza]
spoe-agent coraza-agent
messages coraza-req coraza-res
option var-prefix coraza
option set-on-error error
timeout hello 100ms
timeout idle 2m
timeout processing 500ms
use-backend coraza-spoa
log global
spoe-message coraza-req
args id=unique-id src-ip=src method=method path=path query=query version=req.ver headers=req.hdrs body=req.body
event on-frontend-http-request
spoe-message coraza-res
args id=unique-id version=res.ver status=status headers=res.hdrs body=res.body
event on-http-response
It defines processing timeouts and the messages to exchange via the SPOP protocol.
Thats it for the HAProxy side, lets configure the coraza-spoa service, which
should listen on 127.0.0.1:9000 to exchange the spoe-message with HAProxy.
Coraza Configuration
Coraza SPOA is configured via the /etc/coraza-spoa/config.yml:
log:
# The log level configuration, one of: debug/info/warn/error/panic/fatal
level: info
# The log file dir of the coraza-spoa
dir: /var/log/coraza-spoa
spoa:
# The SPOA server bind address
bind: "127.0.0.1:9000"
# Get the coraza.conf from https://github.com/corazawaf/coraza
#
# Download the OWASP CRS from https://github.com/coreruleset/coreruleset/releases
# and copy crs-setup.conf, the rules & plugins directories to /etc/coraza-spoa
include:
- /etc/coraza-spoa/coraza.conf
- /etc/coraza-spoa/crs-setup.conf
- /etc/coraza-spoa/rules/*.conf
# The transaction cache lifetime(ms)
transaction_ttl: 60000
# The transaction cache limit
transaction_active_limit: 100000
Since Coraza SPOA is only a daemon which exchanges SPOP protocol messages with HAProxy, the configuration is quite simple.
Coraza SPOA also embeds the Coraza Engine and the
OWASP Coreruleset, which are configured by the files
listed in the include section:
- /etc/coraza-spoa/coraza.conf - Coraza Engine Configuration
- /etc/coraza-spoa/crs-setup.conf - Core Ruleset Main
- /etc/coraza-spoa/rules/*.conf - Core Ruleset Rules
- /etc/coraza-spoa/plugins/*.conf - Core Ruleset Plugins
Once the coraza-spoa daemon is running you can begin with the Coraza Engine and Coreruleset configuration.
HELP
If you need help & support you could check the #coraza channel in the OWASP Slack: https://owasp.org/slack/invite